Working with Repositories
Master the art of pulling, committing, and pushing branches.
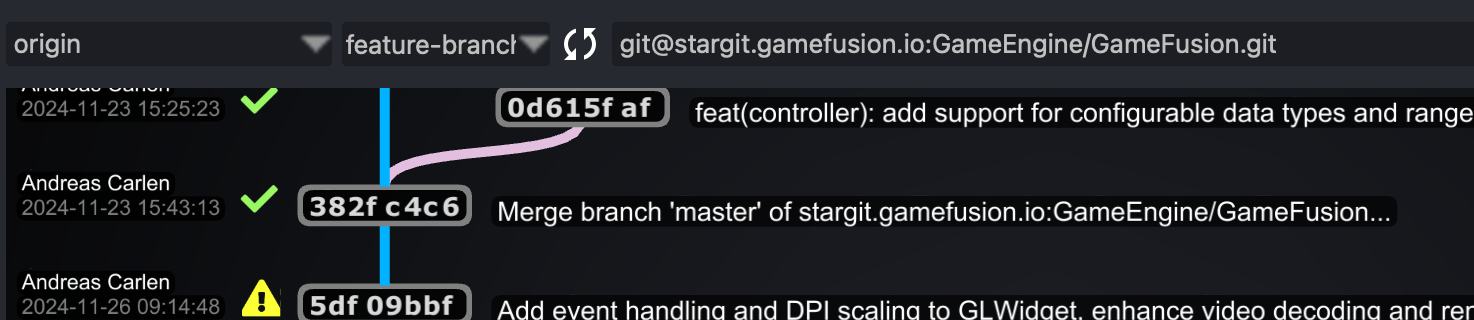
Pulling Changes: Stay updated with the latest changes from your team by pulling updates from the remote repository. Use the "Pull" button in the dashboard to fetch and merge changes seamlessly.
Committing Your Work: Save changes to your repository by creating commits. StarGit provides an intuitive interface to write detailed commit messages, preview changes, and finalize them with a single click.
Pushing Updates: Once your work is ready, use the "Push" button to upload your changes to the remote repository, ensuring that your teammates are on the same page.
Working with Branches
Branch management is essential for any collaborative Git workflow. This section covers the basics: creating, switching, pulling, and pushing branches.
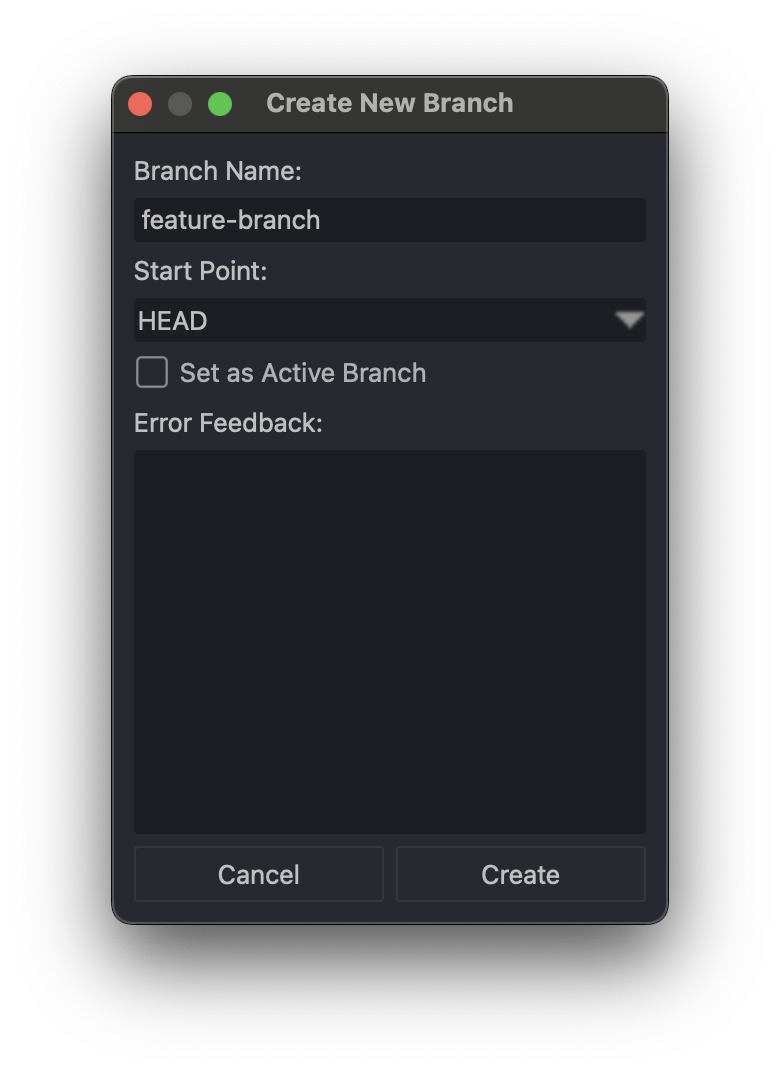
Creating a Branch
A branch in Git is a lightweight movable pointer to a commit. It's an excellent way to work on features, bug fixes, or experiments without affecting the main codebase.
To create a new branch:
- Step 1: Use the command
git branch <branch-name>. - Step 2: Switch to the new branch using
git checkout <branch-name>orgit switch <branch-name>. - Step 3: Start working in your branch. Changes will only affect this branch.
Pro Tip: Always name your branches meaningfully, such as feature/login-page.
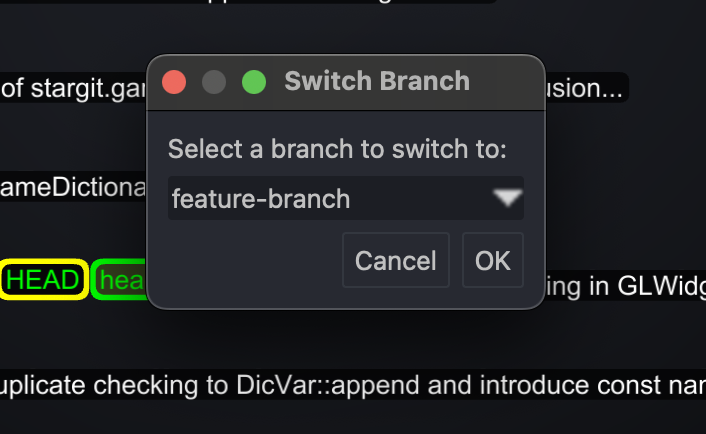
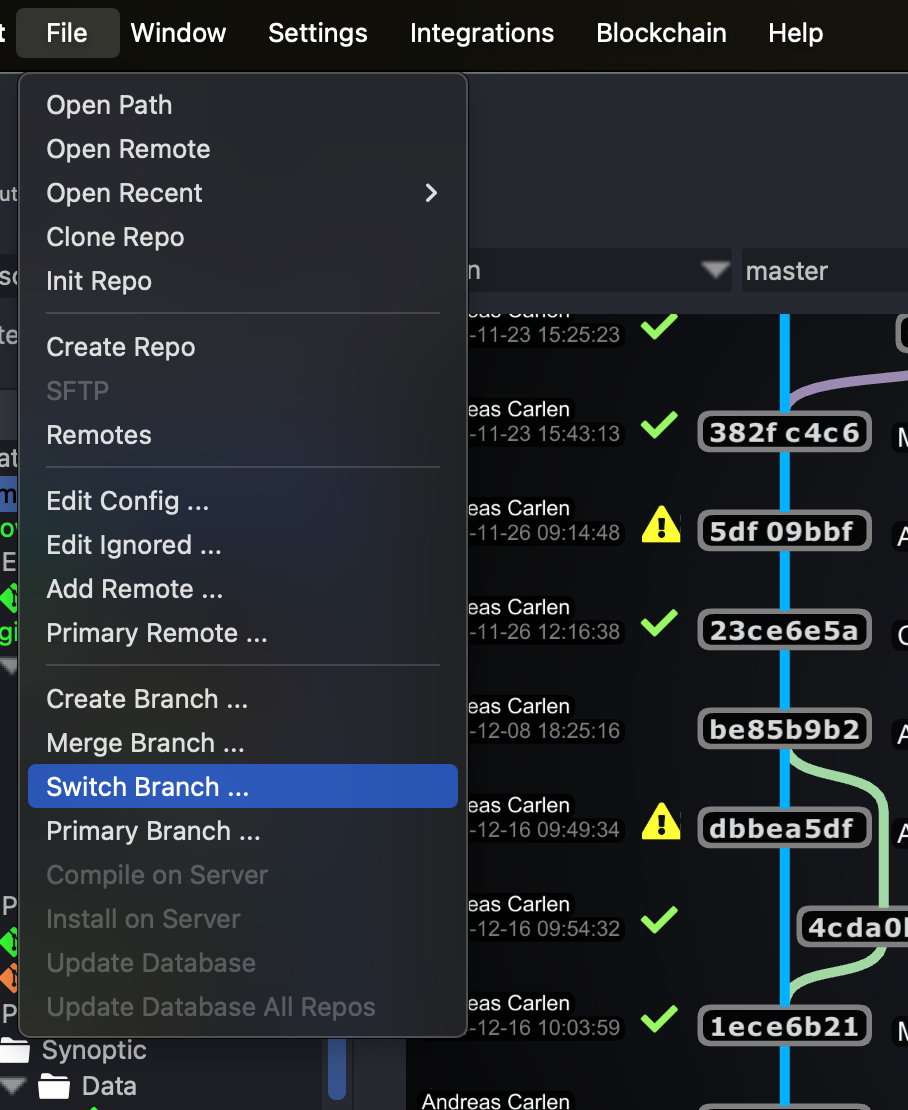
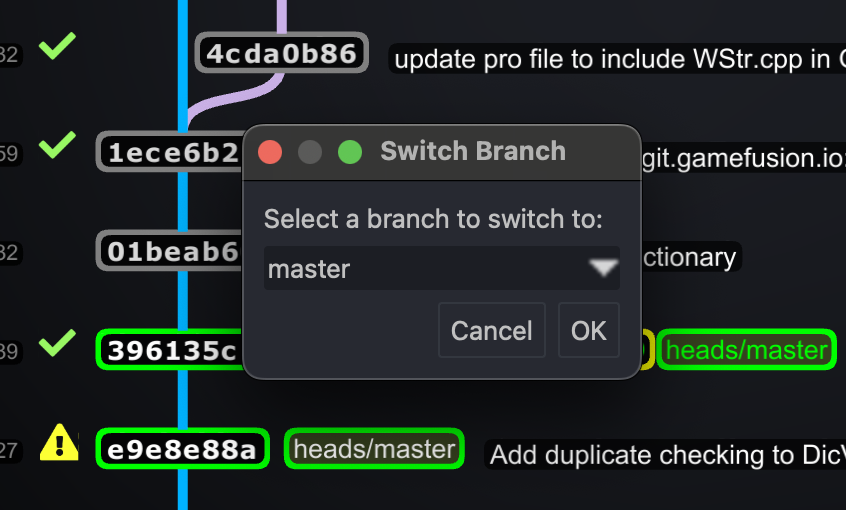
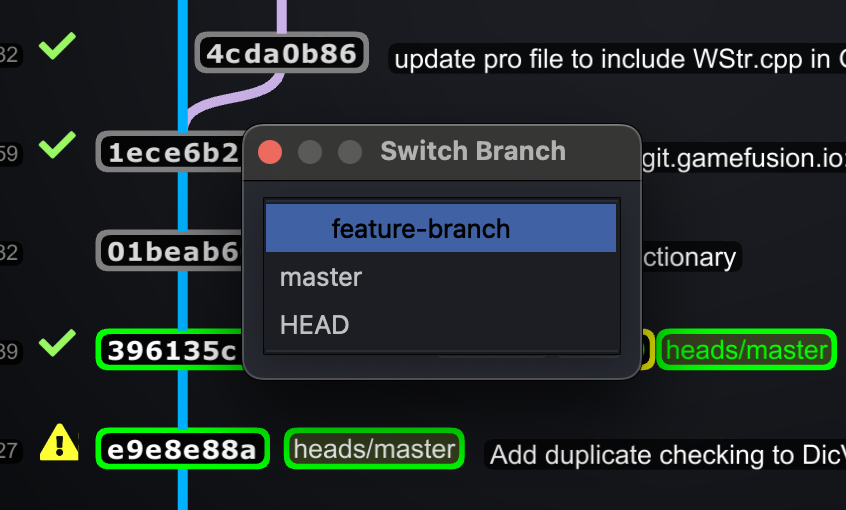
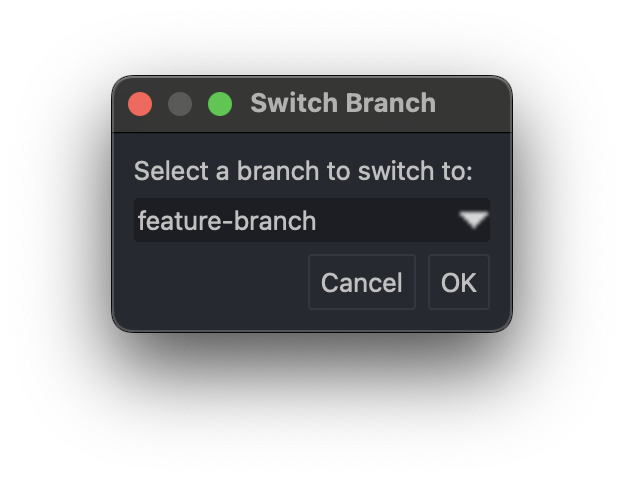
Switching Between Branches
Switching between branches in Git is seamless. It allows you to move your workspace to another branch without affecting other branches.
To switch to a different branch:
- Use the command
git checkout <branch-name>orgit switch <branch-name>. - Ensure your current branch has no uncommitted changes, or use
git stashto save them temporarily. - After switching, your working directory reflects the state of the new branch.
Pro Tip: Use git branch to see all available branches and the one you’re currently on.
Pulling and Pushing Branches
Once you've worked on a branch, you may need to share your changes or retrieve updates from others. This involves pulling and pushing branches.
Pulling a Branch:
- Use
git pull origin <branch-name>to fetch and merge updates from a remote branch. - Ensure you're on the correct branch before pulling updates.
Pushing a Branch:
- Use
git push origin <branch-name>to share your local branch with the remote repository. - If the branch doesn’t exist remotely, Git creates it automatically during the first push.
Pro Tip: Use git push -u origin <branch-name> to set the branch’s upstream, allowing you to omit the remote and branch name in future pushes.
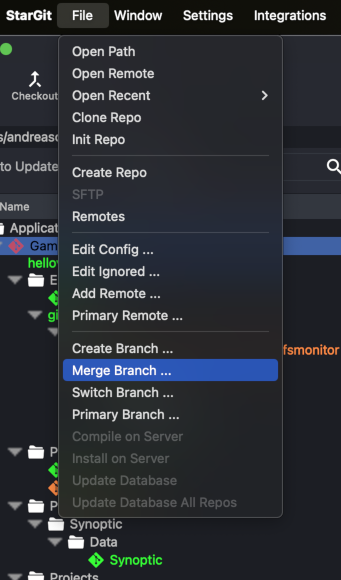
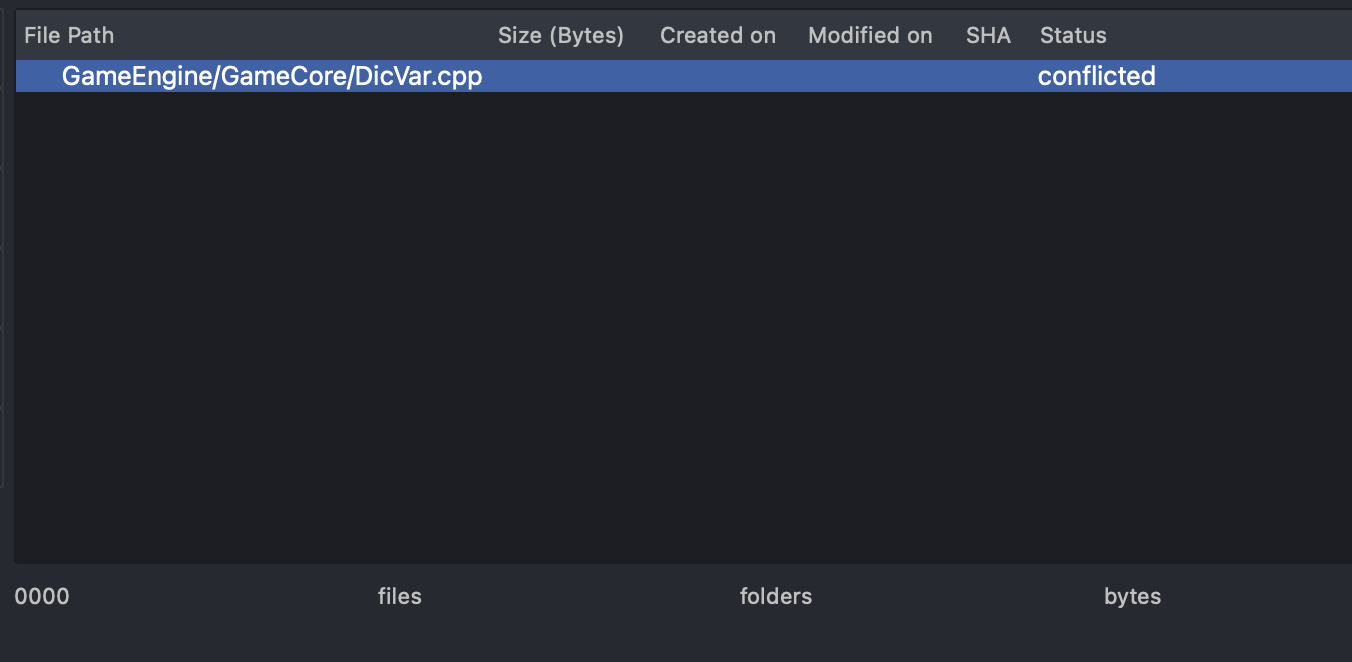
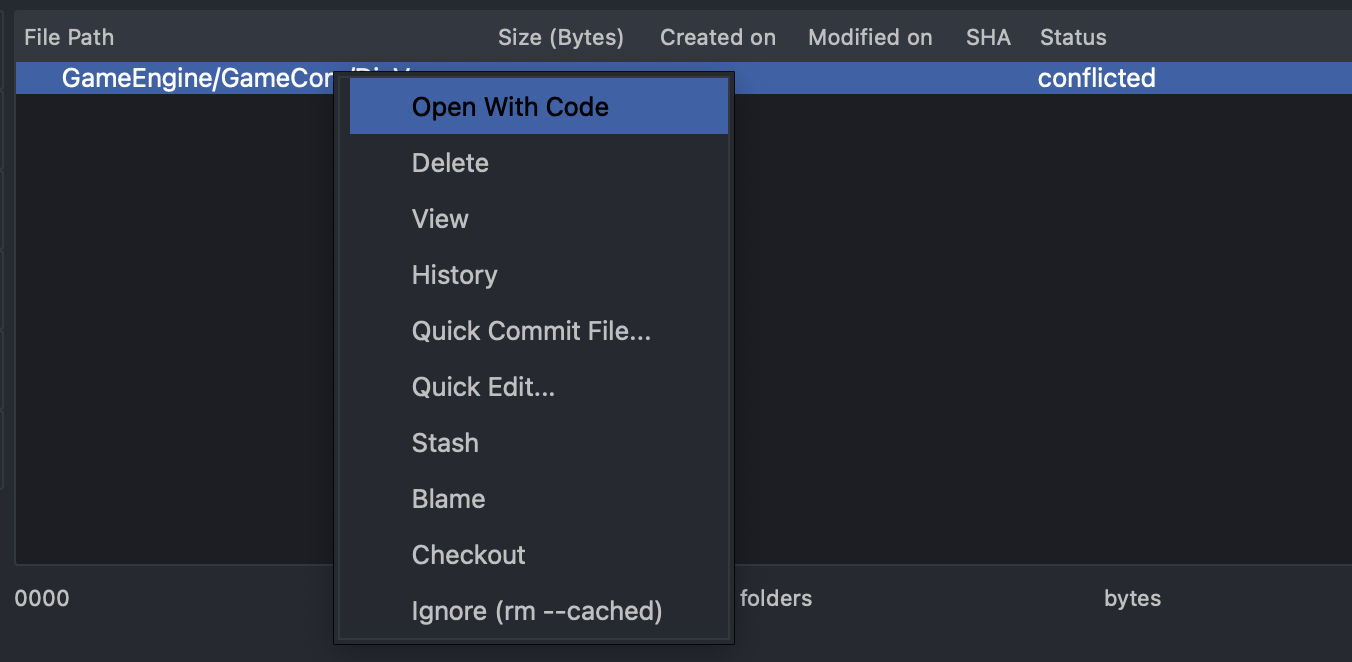
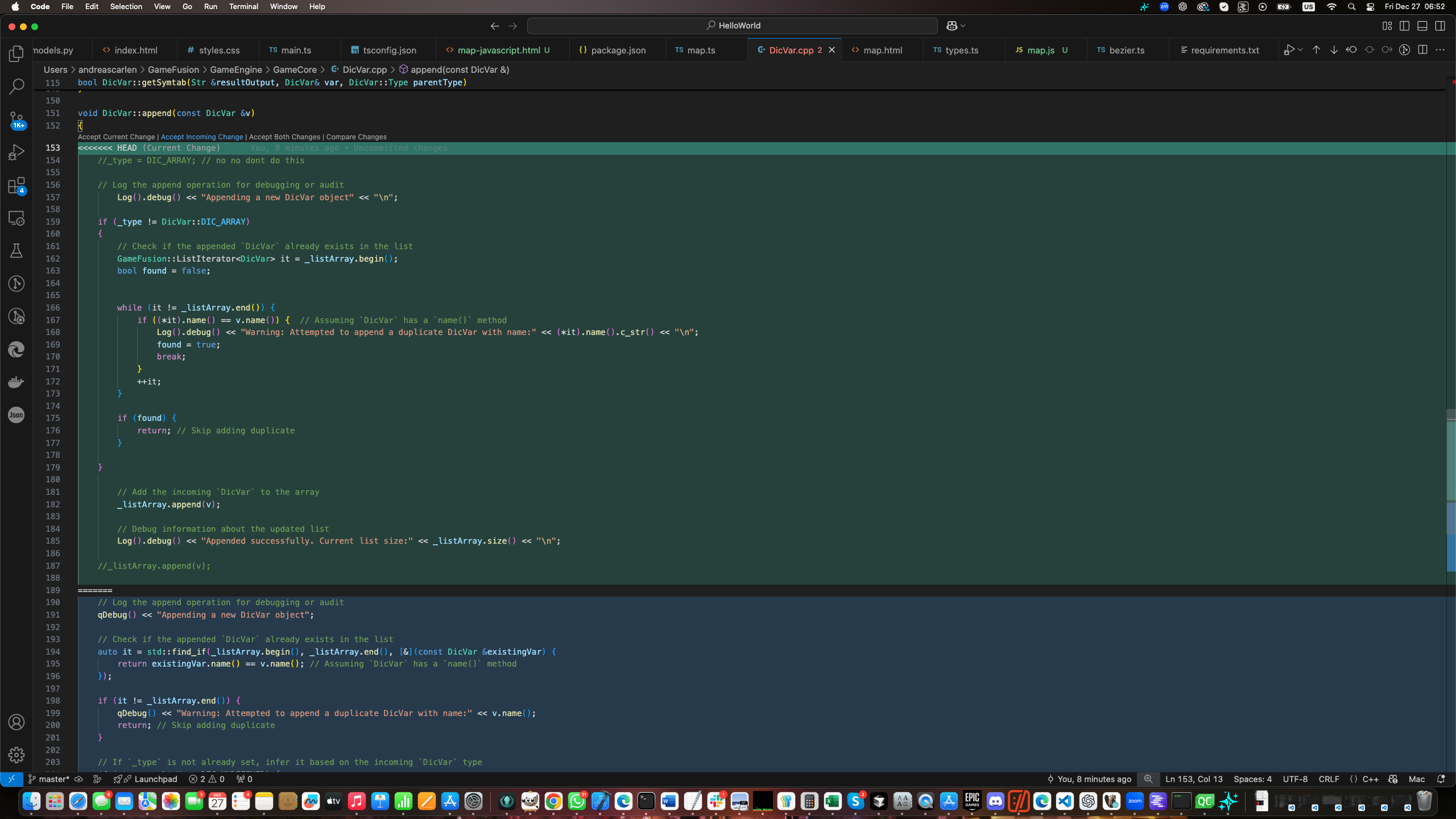
Merging and Conflict Resolution
Merging changes from different branches is common in collaborative projects. Here’s how StarGit makes this process simple and efficient:
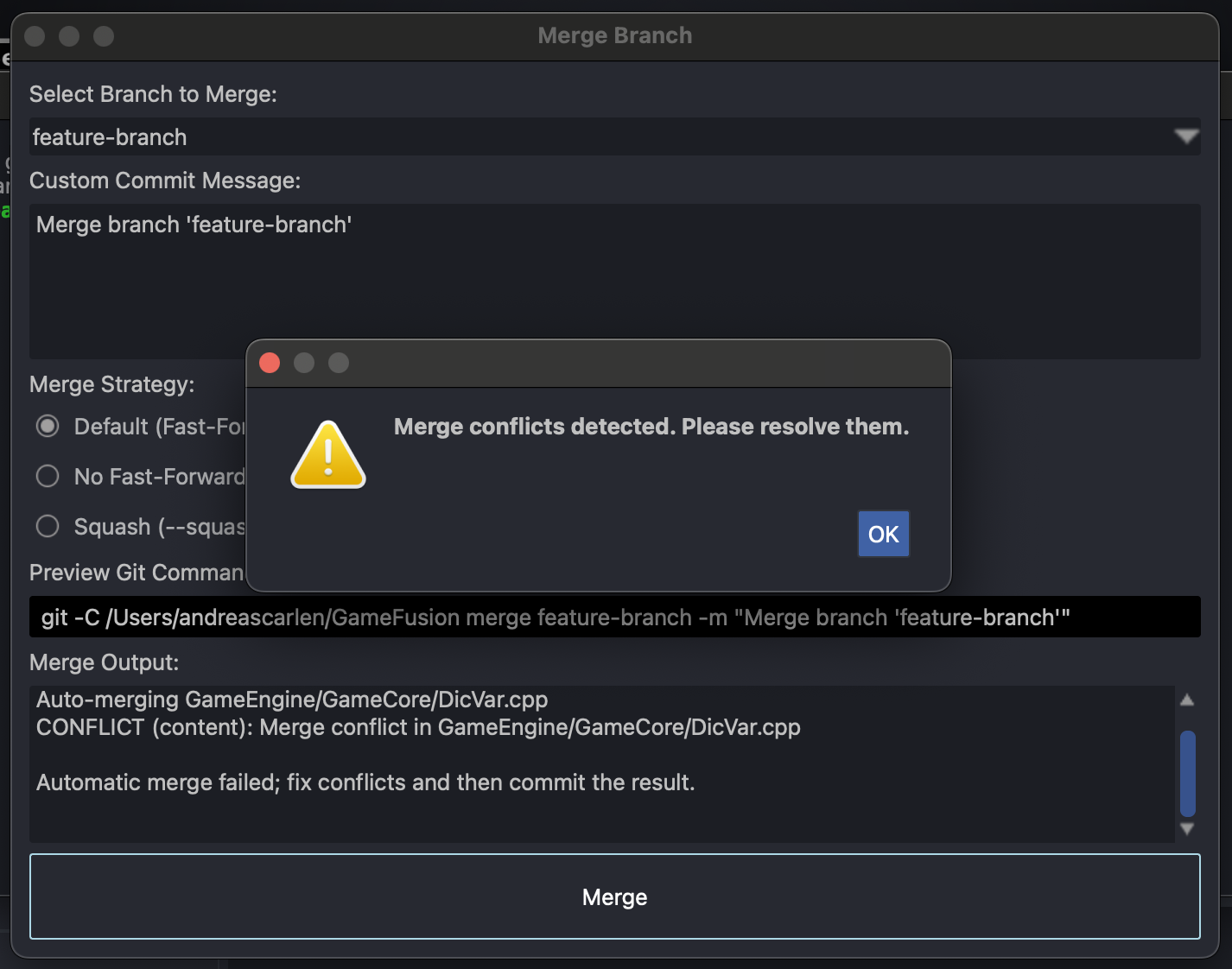
- Initiate a Merge: Select the branch you want to merge into your current branch and click "Merge."
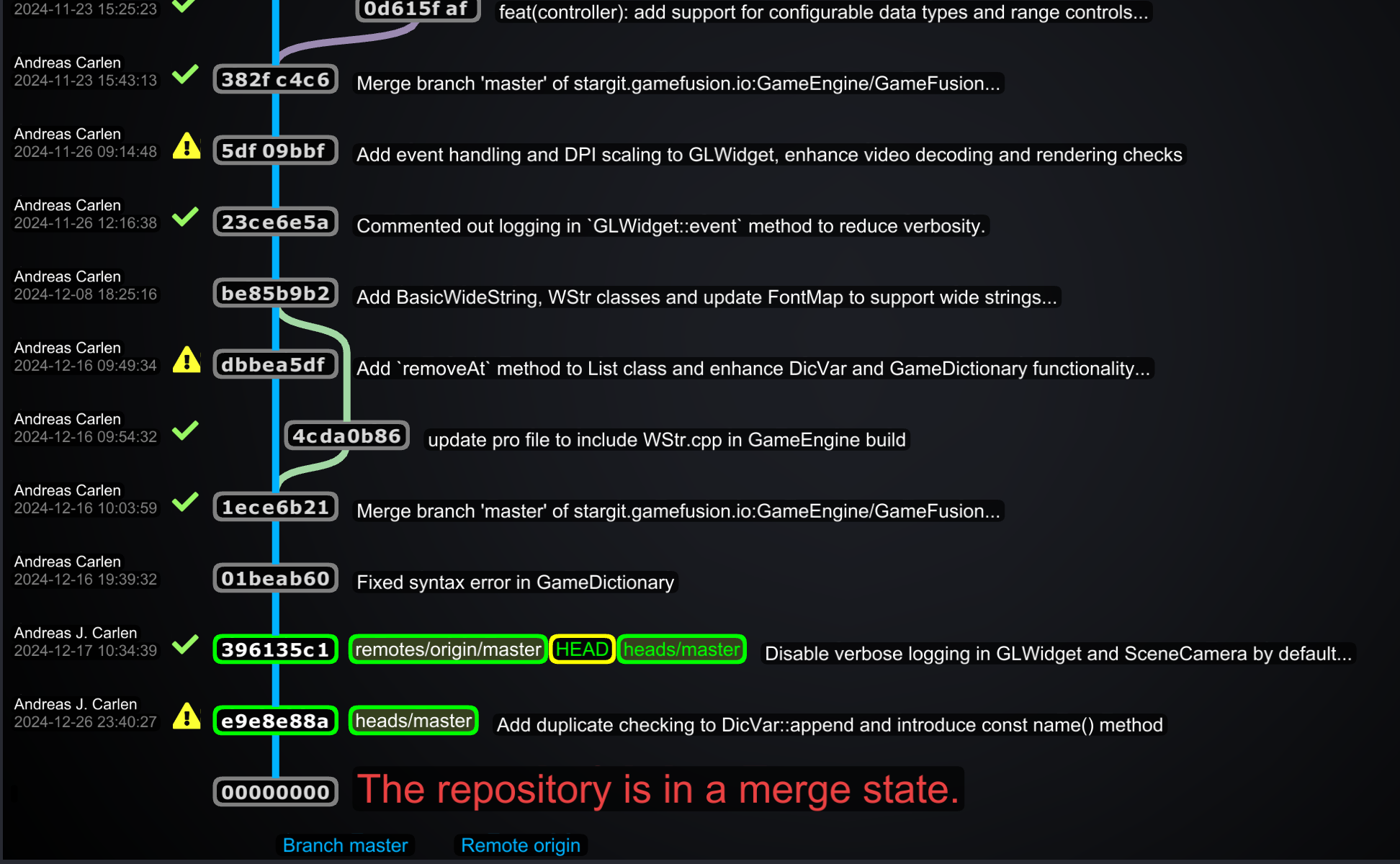
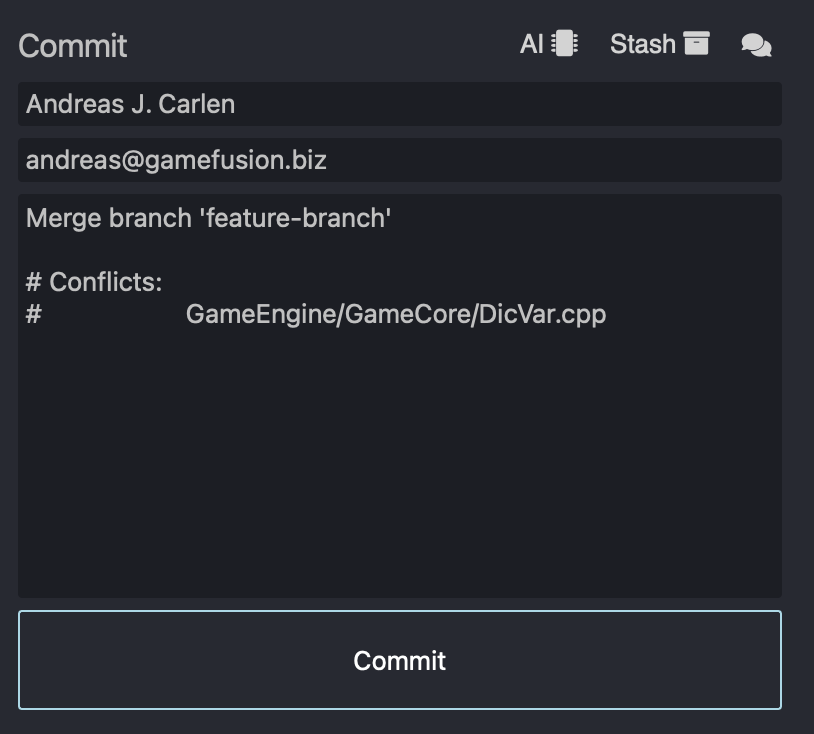
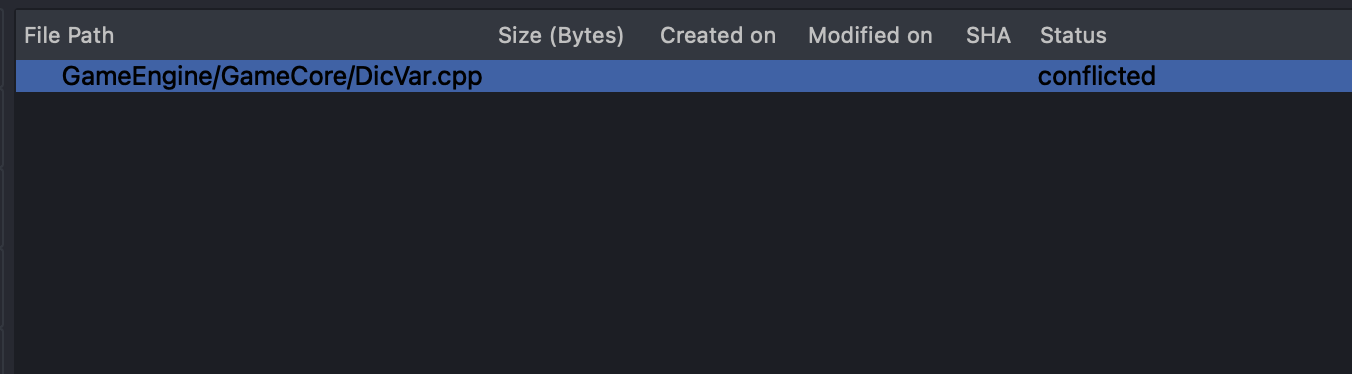
- Resolve Conflicts: If conflicts arise, StarGit highlights the conflicting lines and provides tools to manually or automatically resolve them.
- Finalize the Merge: Once conflicts are resolved, finalize the merge to integrate changes seamlessly.